- ISO 9001:2015 Certified Hospital
- starhospitaludaipur@gmail.com
- +919660713450
- +91 9928569121
PCOD vs PCOS: What Is the Difference, Symptoms, and Full Form Explained

PCOD और PCOS क्या होता है? कारण, लक्षण, अंतर और इलाज पूरी जानकारी हिंदी में
December 13, 2025What Is PCOD and PCOS?
Before jumping into the difference between PCOS and PCOD, it is important to clearly understand what these two terms actually mean. Many people think PCOS and PCOD are same, but that is not true. They are related conditions, but they are not identical.
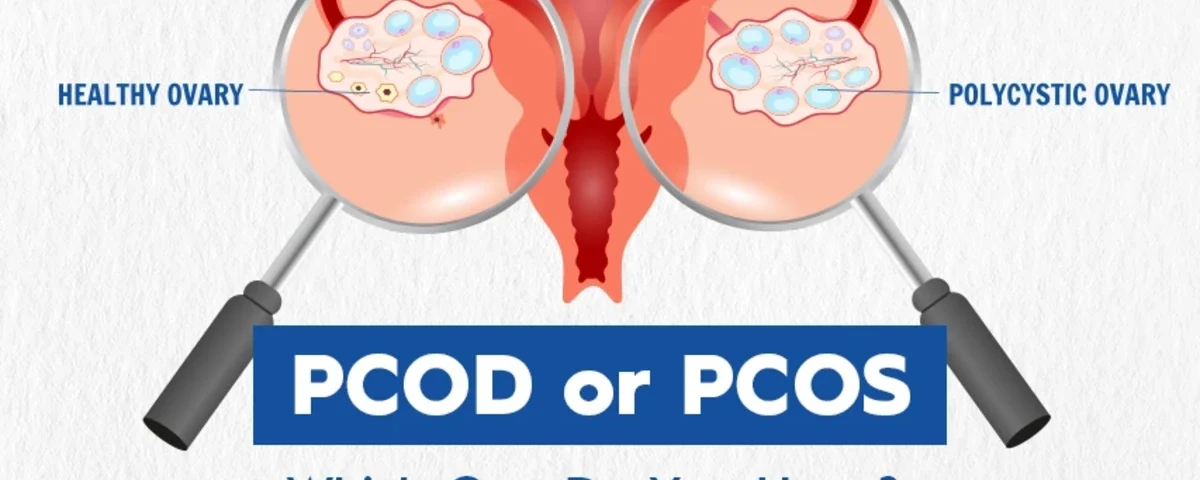
PCOD full form is Polycystic Ovarian Disease.
PCOD happens when a woman’s ovaries release immature or partially mature eggs. Over time, these eggs can turn into cysts. PCOD is mostly linked to lifestyle factors like poor diet, stress, lack of exercise, and weight gain. In many cases, PCOD can be managed and even reversed with lifestyle changes.
PCOS full form is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
PCOS is a hormonal disorder where the body produces excess androgens (male hormones). This affects ovulation, periods, and metabolism. PCOS is considered more complex and long term compared to PCOD and often needs medical management along with lifestyle changes.
At this stage, it is important to clear one common doubt: PCOS and PCOD are same is a myth. They are different conditions with different severity levels. This confusion is also why people frequently search for what is difference between PCOD and PCOS or PCOD and PCOS difference.
In simple terms:
- PCOD is more about ovarian dysfunction and lifestyle impact
- PCOS is a broader hormonal syndrome affecting the whole body
Understanding this basic meaning helps make sense of the difference between PCOS and PCOD symptoms, fertility impact, and treatment approach, which will be explained in the next sections.
Are PCOD and PCOS the Same?
No, PCOD and PCOS are not the same.
This is the clearest answer to the common question “PCOS and PCOD are same?” They are related conditions, but there is a real and important difference between PCOD and PCOS.
PCOD is mainly a condition linked to ovarian function. It usually develops due to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, stress, weight gain, or lack of physical activity. Many women with PCOD still ovulate regularly and can manage the condition with lifestyle changes alone.
PCOS, on the other hand, is a hormonal disorder that affects the entire endocrine system. It involves higher levels of male hormones, irregular ovulation, and metabolic issues. PCOS is considered more severe and often needs long-term medical monitoring.
So, if you are asking what is difference between PCOD and PCOS, the simple answer is this:
PCOD is a milder condition mainly affecting the ovaries, while PCOS is a complex hormonal syndrome affecting the whole body.
Difference Between PCOD and PCOS
Understanding the difference between PCOD and PCOS is important because both conditions affect the ovaries but in different ways. Many people search for PCOD and PCOS difference or even type different between PCOS and PCOD because the symptoms often look similar at first. The table below explains the key differences clearly and simply.
| Basis | PCOD | PCOS |
| Severity | PCOD is usually a milder condition. Symptoms are often manageable with lifestyle changes. | PCOS is more severe and is considered a hormonal disorder that needs long-term care. |
| Hormonal Imbalance | Hormonal imbalance is present but usually mild and limited. | Hormonal imbalance is significant, with higher male hormone levels affecting the body. |
| Ovarian Function | Ovaries release immature eggs that may form small cysts over time. | Ovaries often fail to release eggs regularly, leading to multiple cysts. |
| Long-Term Health Impact | Long-term health risks are lower if PCOD is managed early. | PCOS can increase the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and fertility issues. |
In simple terms, the difference between PCOD and PCOS lies in severity, hormonal impact, and long-term health effects. PCOD is often reversible with lifestyle improvements, while PCOS usually requires ongoing medical management. This clear PCOD and PCOS difference helps patients understand why diagnosis and treatment plans may vary.
Difference Between PCOS and PCOD Symptoms
Although PCOD and PCOS are related, there is a clear difference between PCOS and PCOD symptoms. Many women experience overlapping signs, which creates confusion. Understanding the symptoms of PCOD and PCOS separately makes it easier to identify the condition early and seek the right treatment.
Common Symptoms of PCOD
- Irregular periods, but cycles may still occur
- Weight gain, mostly due to lifestyle factors
- Mild acne or oily skin
- Hair thinning or mild hair fall
- Occasional pelvic discomfort
- Fatigue caused by hormonal imbalance
PCOD symptoms are usually milder and often improve with weight control, healthy diet, and regular exercise.
Common Symptoms of PCOS
- Very irregular or missed periods
- Difficulty in ovulation and fertility issues
- Excess facial or body hair growth
- Severe acne and oily skin
- Rapid weight gain and difficulty losing weight
- Dark patches on skin, especially around neck or underarms
- Mood changes and low energy levels
These symptoms show the difference between PCOS and PCOD symptoms, with PCOS having a stronger hormonal and metabolic impact on the body.
Why Is PCOS Considered More Serious Than PCOD?
PCOS is considered more serious than PCOD because it affects more than just the ovaries. While PCOD mainly impacts ovarian function, PCOS disrupts the entire hormonal system. This increases the risk of long-term health problems such as type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, heart disease, and infertility.
Another key reason is insulin resistance, which is common in PCOS but less frequent in PCOD. This makes PCOS harder to manage and often requires medical treatment along with lifestyle changes.
In short, PCOD is usually manageable and sometimes reversible, but PCOS needs continuous monitoring. This difference explains why doctors treat PCOS as a more complex and serious condition.
PCOD vs PCOS: Impact on Periods and Fertility
One of the biggest real-life concerns for women is how these conditions affect periods and the ability to conceive. When comparing PCOD vs PCOS, the impact on menstrual cycles and fertility is not the same.
In PCOD, periods may be irregular, but many women still ovulate. Delays in cycles are common, yet the body often responds well to lifestyle changes. Weight management, physical activity, and stress control can help restore more regular periods over time. Fertility issues in PCOD are usually temporary, and many women conceive naturally once their cycles improve.
In PCOS, menstrual irregularity is more severe. Periods may be very infrequent or stop completely due to lack of ovulation. Hormonal imbalance and insulin resistance make conception more difficult. Fertility is possible with PCOS, but it often requires medical support, cycle monitoring, or assisted treatment. This clear difference explains why PCOS is usually diagnosed earlier in fertility clinics.
In simple terms, PCOD may delay pregnancy, while PCOS can actively interfere with ovulation if not managed properly.
PCOD vs PCOS: Treatment and Management Approach
When comparing PCOD vs PCOS, the biggest difference in treatment lies in how much each condition depends on lifestyle changes versus medical support. It is important to be clear from the start that there is no permanent cure for either PCOD or PCOS, but both can be managed effectively with the right approach.
In PCOD, treatment is largely lifestyle-driven. Improving daily habits plays a major role in symptom control. A balanced diet, regular exercise, weight management, proper sleep, and stress reduction often help regulate periods and reduce symptoms. Medicines, if prescribed, are usually short term and focused on managing specific issues like irregular cycles or acne. Many women with PCOD see significant improvement once lifestyle changes are consistent.
In PCOS, management usually requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment. Since PCOS involves hormonal imbalance and metabolic issues, doctors may prescribe medicines to regulate periods, manage insulin resistance, or support ovulation when pregnancy is planned. Lifestyle changes are still essential, but PCOS often needs long-term monitoring and treatment adjustments under medical guidance.
Because symptoms and health risks vary from person to person, consulting an experienced specialist is important. A qualified Gynecologist in Udaipur at Star Hospital can help create a personalized treatment plan based on symptoms, age, and fertility goals. For women seeking advanced care related to reproductive and hormonal health, services like Hormonal Treatment may also be part of a broader treatment discussion.
The key takeaway is simple: PCOD is more responsive to lifestyle correction, while PCOS usually needs consistent medical support along with healthy habits. Early diagnosis and the right management approach make a big difference in long-term health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between PCOD and PCOS?
The main difference between PCOD and PCOS lies in severity and hormonal impact. PCOD is usually a milder condition related to ovarian dysfunction and lifestyle factors. PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects ovulation, metabolism, and long-term health. PCOS often needs continuous medical management, while PCOD can improve with lifestyle changes.
Are PCOD and PCOS the same?
No, PCOD and PCOS are not the same. Although both affect the ovaries and cause irregular periods, PCOD is less severe and mainly lifestyle-related. PCOS is a complex hormonal condition involving excess male hormones and insulin resistance.
Which is more serious, PCOD or PCOS?
PCOS is considered more serious than PCOD. It has a stronger effect on hormones, fertility, and metabolism, and it can increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease if not managed properly. PCOD is usually easier to control and may be reversible in many cases.
Can women with PCOD or PCOS get pregnant?
Yes, women with PCOD or PCOS can get pregnant. In PCOD, fertility often improves with healthy lifestyle changes. In PCOS, pregnancy is possible but may require medical support to regulate ovulation. Early diagnosis and proper management greatly improve chances of conception.